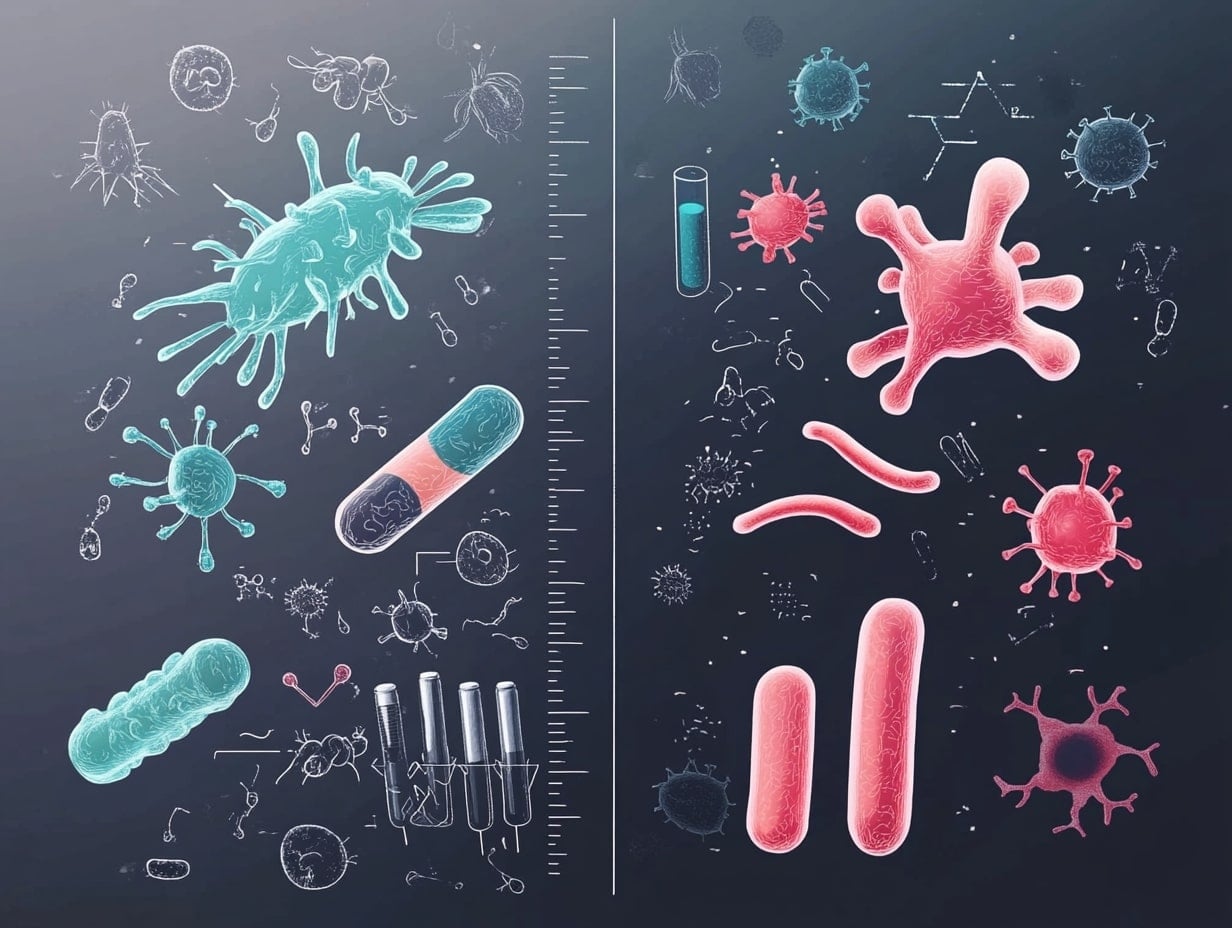
What’s the Difference Between Bacterial and Viral STDs? Explained
Jan 30, 2025
Bacterial STDs, like chlamydia and gonorrhea, are treated with antibiotics, while viral STDs, like HIV and herpes, are managed with antiviral medication. Bacterial STDs can typically be cured, while viral STDs are lifelong but manageable with proper treatment. Both types require regular testing and safe sex practices to prevent transmission.
Bacterial STDs
Common Bacterial STDs: Some of the most common bacterial STDs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. These infections are caused by bacteria and are typically transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. They often cause inflammation, pain, and discharge, but some individuals may have no symptoms at all.
Treatment of Bacterial STDs: Bacterial infections can usually be treated with antibiotics. If diagnosed early, most bacterial STDs are treatable and curable. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure that the infection is fully eradicated. If left untreated, bacterial STDs can lead to serious health complications, such as infertility, chronic pain, or organ damage.
Symptoms of Bacterial STDs: Common symptoms include unusual discharge from the genitals, burning sensation during urination, or sores and bumps around the genital area. However, many people may not experience any symptoms, which is why regular testing is essential.
Viral STDs
Common Viral STDs: Viral STDs include infections such as HIV, herpes (HSV-1 and HSV-2), human papillomavirus (HPV), and hepatitis B. Unlike bacterial infections, viral infections cannot be completely cured. However, they can often be managed with antiviral medications that help control symptoms, reduce the frequency of outbreaks, and lower the risk of transmission.
Treatment of Viral STDs: While there is no cure for viral STDs, medications such as antiretrovirals for HIV and antivirals for herpes can help suppress the virus and reduce its impact on your health. Vaccines are available for some viral infections, such as HPV and hepatitis B, which can help prevent infection in the first place.
Symptoms of Viral STDs: Viral STDs often cause sores, rashes, or flu-like symptoms, but some may not present any symptoms at all. For example, HPV may cause no symptoms but can lead to cervical cancer or other types of cancer if not detected and treated early.
Key Differences Between Bacterial and Viral STDs
Cure vs. Management: Bacterial STDs can usually be cured with antibiotics, while viral STDs can only be managed through medication and preventive measures.
Treatment Approach: For bacterial infections, antibiotics effectively clear the infection. For viral infections, the focus is on managing symptoms, reducing outbreaks, and preventing transmission.
Prevention: Vaccines are available for some viral STDs, such as HPV and hepatitis B. Regular screening and safe sexual practices can help prevent both bacterial and viral STDs.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between bacterial and viral STDs helps you make informed decisions about your health. While bacterial infections are generally treatable and curable with antibiotics, viral infections require long-term management. Regular testing, preventive vaccines, and safe sex practices are essential to protecting yourself from both types of infections.
Dr. Michael Thompson
Dr. Michael Thompson is an expert in sexually transmitted diseases with extensive clinical and research experience. He leads campaigns advocating for early diagnosis and prevention of diseases like HIV and gonorrhea. He collaborates with local organizations to educate both youth and adults about sexual health.